Just as the saying goes, ‘if all you have is a hammer, everything looks like a nail’
Boxiang Wang, Instructors of 2021 LINKS China team.
Understand the Problem & Enphasise
Background Overview
It has been reported that in less than 30 years, antimicrobial drug resistance could be more
deadly than cancer, causing 10 million deaths per year by 20501. As bacterial drug resistance
becomes more prevalent, and even gives rise to bacteria such as MRSA - methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), recognised as a "superbugs", the prevention and treatment of
drug-resistant bacterial infections has become even more critical.
S. aureus is one of the most notorious and prevalent bacterial pathogens, and it has caused
numerous reports of food poisoning, with S. aureus-induced food poisoning accounting for about
25% of foodborne microbial food poisoning incidents2.Common symptoms include acute
gastroenteritis, nausea, severe vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhoea, and occasionally deaths
in young children and the elderly. The contamination of MRSA in commercially available foods in
China is characterised by a wide distribution of contaminated areas and a variety of
contaminated foods, with MRSA detection in foods reported in several provinces and cities, with
relatively high rates of MRSA contamination in raw meat and raw milk; and a slightly lower rate
of contamination in ready-to-eat foods, fruits and vegetables. The prevalence of multi-drug
resistance indicates that the drug-resistant status of food-borne S. aureus in China has become
more serious, posing a potential threat to the safety and health of consumers3.
In the process of investigating the background, we found that for a long time, there is a big
gap between urban and rural medical resources in China, and China is a developing country with a
huge scale of rural areas, and there are a lot of people who do not have access to the treatment
of food poisoning in many places unseen by us. Medical conditions are better in cities, but with
the emergence of drug resistance there are fewer and fewer treatments for MRSA, while in rural
areas, due to the lack of understanding of food poisoning, food poisoning is not taken seriously
enough, and medical resources are backward, making it difficult to get timely and effective
treatment, and there have even been cases of large-scale poisoning from banquets. Due to the
differences in medical conditions, vaccine coverage, and food safety awareness between urban and
rural areas in China, we plan to reach out to stakeholders in both urban and rural areas in
order to gain a more comprehensive understanding of what's on their minds, and to tailor our
programme to meet the needs of people in different regions. We also hope that through our
efforts, we can help people suffer less from illnesses, and make food poisoning treatments
accessible and effective in rural areas of China, so that people can afford to go to the doctor
and have peace of mind.
Questionnaire Survey
In order to obtain first-hand information, get out of the literature and understand people's
thoughts, we conducted a questionnaire survey, referred to iGEM regulations and the "Ethical
Approval Protocol for Biomedical Research involving Humans" issued by the National Health
Commission in 2016, and wrote an informed consent form.
Statistics can lie, and we never want to get questionnaire data that is invalid and
unscientific. Taking inspiration from Dr. Joy Yueyue Zhang's speech at the opening ceremony of
iGEM 2020, she condensed how to interpret social science research into five key points:
Step 1: Be clear about what you want to know
Step 2: Be smart about what type of research you look up
Step 3: Be critical of the sources
Step 4: Be mindful of the context
Step 5: Be reflexive when integrating social studies into your iGEM
project
Combining quantitative research and qualitative research, we designed this questionnaire to
carry out background investigation under GDPR, so as to better understand the situation and
people's opinions in urban and rural areas, so as to adapt our project to a wide range of needs.
In addition, we added knowledge related to food poisoning and synthetic biology to the
questionnaire page, and at the same time served the purpose of education. After discussion
within the group, we decided to conduct questionnaire collection in a small range. After testing
the questionnaire in the group, we released the questionnaire in July.
click here to view the survey results.
The results show that in rural areas, the proportion of people suffering from gastrointestinal
diseases is higher, which may be related to cultural background and economic status, under this
premise, food poisoning will have a greater impact on them, and we find that the proportion of
people who do not think of food poisoning when they have gastrointestinal discomfort or similar
discomfort symptoms is as high as 88%, which corresponds to the data of the other question. The
proportion of people who did not know about food poisoning caused by Staphylococcus aureus and
related prevention knowledge was also 88%. It is not difficult to imagine that the lack of
relevant knowledge makes them often ignore food poisoning and intestinal health. We hope to
carry out more publicity on intestinal health. Some people found that they could not get timely
treatment after food poisoning, and they reported that it was due to insufficient medical
resources. According to our field investigation, the most common treatment for bacterial food
poisoning in these areas is intravenous antibiotic injection, but the abuse of antibiotics will
lead to decreased immunity and can not treat drug-resistant bacteria such as MRSA. It's very
difficult to treat them once they get a disease like that, and that's one of the reasons why we
initially wanted to make the program into a vaccine form, a capsule form of antibacterial drugs
that could be better delivered to these areas and help a wide range of people, and we realized
that this form was very necessary.
In urban areas, food poisoning is also more common. Fortunately, most of them can be treated in
time. The few who are not treated in time are not paid enough attention to food poisoning caused
by MRSA, which shows the importance of education.
Among the survey population, we found that half of the public have little understanding of
synthetic biology. Considering that there are fewer questionnaires and more people don't know
about synthetic biology, we consider organizing educational publicity activities about synthetic
biology in the form that everyone prefers in the questionnaire, including science education,
tiktok publicity, etc. At the same time, we will also adopt more interesting ways to promote
education, which can not only increase the public's knowledge, but also help our projects to be
more smoothly applied to reality. Please refer to the Education
section for
details.
To our surprise, the results showed that people generally accepted genetically modified drugs
at present, and they would use them as long as they were confirmed to be safe and have good
therapeutic effects, which gave us the confidence to carry out the project and the determination
to start the entrepreneurial part.
We sincerely thank the participants of this questionnaire, whose valuable responses helped us
understand the context and the practical issues that need to be addressed. Due to time
constraints, we prepared the questionnaire as soon as possible to save enough time to collect
responses. Then we conducted spss reliability analysis on the questionnaire results and realized
that there were still many imperfections in the questionnaire, which did not fully play its
role. We learned the relevant knowledge of market research and designed version 2.0 based on the
feedback of the fillers after discussing with relevant experts. Can more accurately and
comprehensively investigate background and gather information,Click here for version 2.0 of the
questionnaire
But after all, the questionnaire cannot give us more detailed feedback and suggestions. What do
they need our drugs to do? What can we do to allay this concern? What are the real needs of
health clinic doctors and patients in rural areas today? We plan to conduct in-depth interviews
with more relevant stakeholders to obtain feedback to improve the project.
Deep contact with residents in rural and urban communities
Due to time constraints, I selected two representative stakeholders from rural areas and urban
areas
for interview, and we signed informed consent with them. The following content is presented
after
consent.
Village:
Health clinic doctor, no investigation.
City: City: Patients with gastrointestinal disease, not investigated.
Define A Good Solution
Based on our background checks and conversations with people in urban/rural communities, we
learned a lot of background knowledge about food poisoning caused by MRSA, and we couldn't help
but wonder, what would be a good solution? We thought it was important to incorporate the voices
of our stakeholders and incorporate their needs into our project, and then we considered the
values that the project should follow and identified the solution.

Figure 1 What would a good solution look like?
Values
Values will guide all the work of human practice, so it is very important to determine what our
values are at the beginning. After understanding what our solution should be, we discussed the
values that the project should follow in the 2.1 group meeting, which are responsibility,
equality, safety and innovation respectively.
Regarding safety and innovation, we believe that an unsafe project is bound to be irresponsible,
and a project that adopts the wisdom of the predecessors is bound to be a bad project, so these
two points must be incorporated into the values to guide the design and development of the
project.
Our ultimate priority values are responsibility and equality. No matter how high a
project
flies, we always believe that it must be responsible, we need to make a positive impact on the
world, friendly dialogue with stakeholders, every detail of the project permeates this concept,
which is our core value; At the same time, we also aspire to equality, we are well aware that we
live in a huge gap, different levels of development in different regions, social and economic
inequality, but we ignore that everyone is equal in front of life, if our project can
contribute
to the contribution of medical treatment to solve the inequality, it will be a great achievement
for us, we will try to lower the price, Patents are filed so that they will not be used for
undesirable purposes, and we expect that socioeconomic equality and the quality of life of
individuals will also be improved, and that low-cost, user-friendly drugs will be developed for
use by patients
Synthetic Biology as the Solution
After understanding the needs of our stakeholders and identifying our values, we decided on
synthetic biology as the solution. In the context of MRSA's development of resistance to
multiple antibiotics, synthetic biology solutions are currently a suitable solution and we will
implement them in a responsible manner. Engineered bacteria super eco will not make MRSA
resistant, and will secrete antimicrobial peptides to kill MRSA efficiently and accurately when
encountering MRSA. It will no longer be a dream that the intestinal tract will be far from the
poison of MRSA, but it will become possible through our efforts.
In addition, synthetic biology allows us to meet the needs of our stakeholders, and it has the
potential to become a safe and efficient solution, with the potential to alleviate inequalities
in healthcare resources and maintain gut health in the future. In our questionnaire survey, most
people are willing to accept genetically modified drugs as long as they are confirmed to be safe
and efficient, so our solution has a good market prospect.
Overall, our synthetic biology program is values-oriented and people-centered, and it provides a
solution that is responsible and beneficial to the world and is a program worth exploring.
Project Shaping
Continuous Engagement with Stakeholders
No one person or group of experts was smart enough to accurately anticipate the positive and
negative impacts of developing technologies, and at the outset our team came to a consensus that
we should listen to the world rather than work stubbornly blindfolded.
2.1 We conducted a stakeholder brainstorm in the group, reflecting on several fields including
science, business, application crowd, government and ethics. We compiled the stakeholders we
thought of into Mendolow's matrix. Due to limited time and resources, We will mainly contact
high-interest &Power, but at the same time, patients are also a group of people we attach great
importance to, so we will also keep in touch with them, their needs are our first. Constantly
meeting with stakeholders and integrating feedback design processes throughout the process
ensures super eco fully reflects the needs of each participant
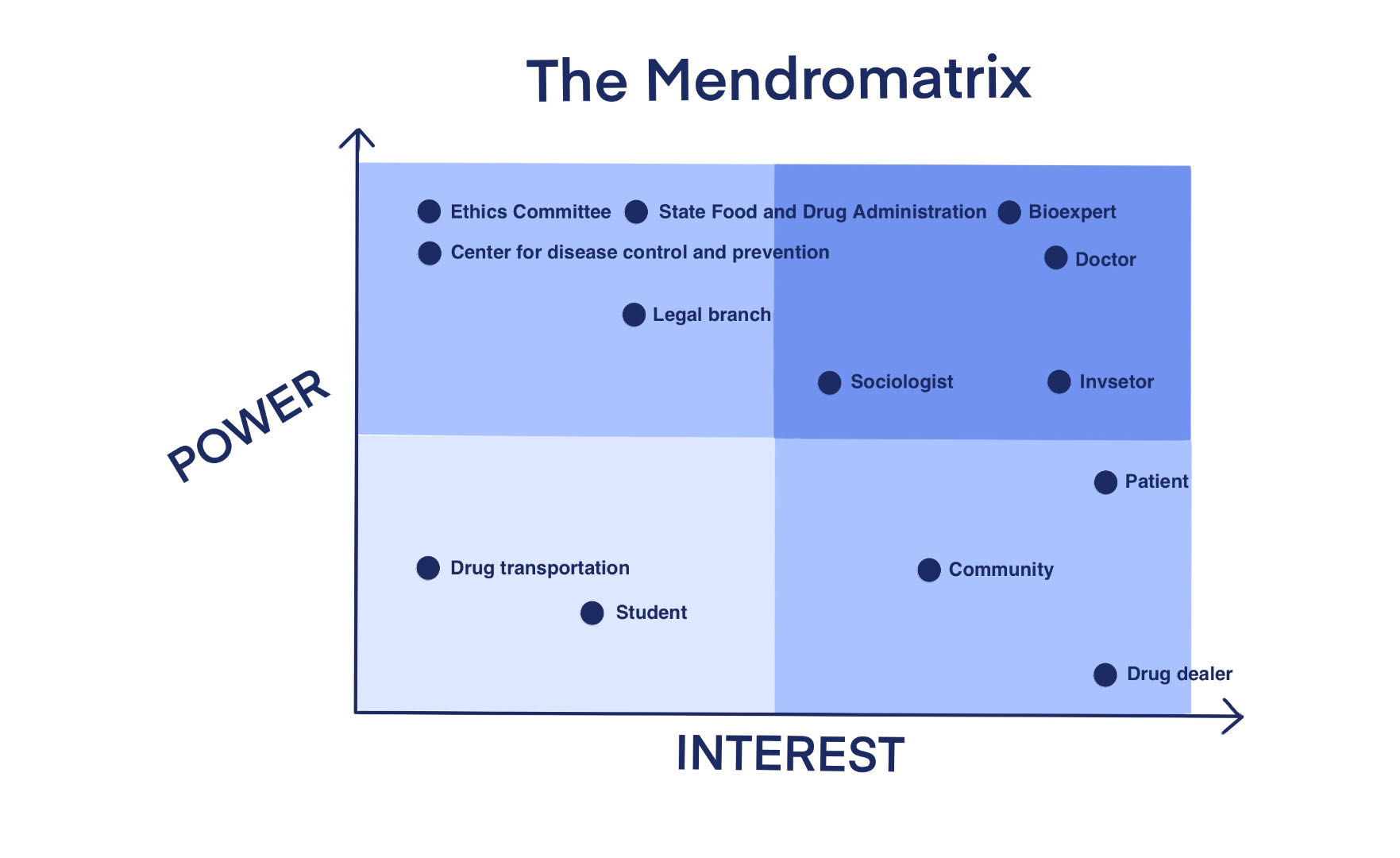
Figure 2 Mendelow’s matrix. The stakeholders of the four parts have different
interests and power. Due to limited time and resources, we will mainly contact with
high-interest &Power to let them fully participate in the project and try our best to meet their
needs. At the same time, patients are a very important group to us, they are low-impact but
important stakeholders, and they need to communicate fully to ensure that there are no problems,
so we also keep in touch with them, their needs are our first priority.
This was followed by an initial engagement with stakeholders. We divide the contact with
stakeholders into four stages: the initial stage of the project, the detailed stage of the project,
the experimental stage, and the keep in touch stage. In each stage, we will adopt the PDCA cycle to
carry out the contact with stakeholders. Please see the
overview page for the specific
introduction
of the PDCA cycle. We recognize that our program may not be a perfect solution to Staphylococcus
aureus food poisoning after several cycles.
However,since we have identified problems in the process, it is our responsibility to continue
to explore solutions in order to meet our responsibilities and commitments. We know that not
every meeting is followed up, and not every plan is implemented, but we cherish and value every
interaction with our stakeholders and reflect carefully on their opinions, and we sincerely hope
that this project will continue to grow and truly help everyone.
Early stage of the project: After selecting the topic, we were not sure whether
Escherichia coli could be successfully colonized in the intestine and whether the addition of
this engineered bacteria would affect the original intestinal microecology, so we contacted
Professor Ying by email. Professor Ying, an expert in microbiology, quickly replied to us,
affirming the feasibility of E. coli colonization, and he suggested that we design experiments
to verify whether E. coli would affect microorganisms and to what extent. We received the
affirmation and became more convinced that our project was feasible. We added hardware design
and related experiments to extract intestinal microbes from mouse feces to simulate intestinal
microecology for testing. Please refer to the hardware page for details.
Figure 3 Email contact with Professor Ying.
Project refinement: not yet expanded. The specific person to contact
depends on the development of the project, and we will contact the experts who can give us
guidance on the problems encountered in the project. The scope of the experts is not limited to
biological experts, but also sociologists, l wyers, entrepreneurs, etc. For example, in the
process of project elaboration, we are not sure whether the design of this step will cause
ethical problems and bring adverse effects on the society. We can reach out to a sociologist and
decide if we want to design this way based on his advice.
Experimental phase: not yet started. Who to contact depends on the development of the
project.
Keep in touch: Not expanded. This part is mainly to verify our project, keep in touch
with the stakeholders we have contacted before, obtain their views on the current stage of the
project, and let them know that the project we have guided is like this. Holding teacher
lectures, industry conferences and inviting everyone to attend are also our plans.
Nothing can be done overnight, stakeholder engagement is not a one-time task, and the
integration of our contact and feedback with stakeholders is a combination of many PDCA cycles,
which continuously hone our project and make it better implemented. Now we have this "hammer" in
our hands, we are eager to find a "nail", but not everyone can change the world, we need to
understand the world first, thank the stakeholders willing to listen to our project, give
suggestions to help it become better.
Future challenges and shortings
1、Staphylococcus aureus poisoning detector: In the process of contact with stakeholders,
we
realized that the project is very limited, if it is not considered as a health product, to know
exactly whether it is staphylococcus aureus poisoning treatment, how can people determine
whether it is staphylococcus aureus poisoning at home? If you need to go to the hospital for
testing, will it make the process difficult? Looking at rural areas, how can health clinics be
equipped to culture colonies to identify staphylococcus aureus poisoning? In view of the above
questions, we decided to develop a convenient staphylococcus aureus detector in the future, so
that people can quickly detect food poisoning at home, the right medicine, so as to
comprehensively solve the problem.
2、extend the colonization time of E. coli. One potential application for super eco is a
vaccine,
but we don't know how long it will take to colonize, preliminary estimates are 10-15 days.
Frequent use of drugs can bring many problems, similar complaints we hear a lot of people around
hypertension and diabetes patients, in order to achieve a permanent cure, in the future, we plan
to find ways to extend the colonization time of E. coli, so that the body is immune to
Staphylococcus aureus for a longer period of time.
Close the Loop
We have considered all technical, safety, ethical and sociocultural issues related to
implementation. Through a broad and thorough understanding of the background, we understand the
background significance of the project, and at the same time, we are more certain about which
direction we should go. The extreme imbalance of medical resources has always been a
contradiction in China. We live in a huge gap. We hope that our project can make a small
contribution to narrowing this gap, and benefit the vast number of developing countries, so that
people can eat with peace of mind, so that areas with backward medical conditions can also have
a convenient way of treatment.
In intergrated humanpractice, in order to continuously improve the project, we have dialogues
with stakeholders in multiple fields and obtained a wide range of opinions. We will constantly
adjust our project according to their feedback, so as to achieve a closed loop of design, so
that our project is not only made behind closed doors. It's the result of extensive
communication.
There is still room for further development and improvement in our human practices, but we have
put a lot of thought and effort into quickly experiencing the entire hp process in this short
one-month period, trying to sense the impact of our program and make it a responsible and humane
program. Now, we can finally say that this project was a less naive idea. Thank you to our team
members and everyone who gave us guidance, suggestions and feedback during the wp process. It is
you who have made this project what it is now. We will not stop and look forward to its future
together!
References
-
Xuan, J., Feng, W., Wang, J., Wang, R., Zhang, B., Bo, L., Chen, Z.-S., Yang, H., and
Sun, L. (2023) Antimicrobial peptides for combating drug-resistant bacterial infections,
Drug Resistance Updates 68, 100954.
-
张从超. (2017) 生牛乳中金黄色葡萄球菌的快速检测及耐药性研究, 齐鲁工业大学.
-
容冬丽, 吴清平, 吴诗, 张菊梅, and 徐明芳. (2018) 我国部分地区即食食品和蔬菜中金黄色葡萄球菌污染分布及耐药和基因分型情况, 微生物学报 58,
314-323.
"I go to the road with ease, I am healthy, I am free, the whole world is spread out before
me, the long loess road can lead me to where I want to go." From then on I no longer want to
be happy, I am happy. "


